Why does my FM transmitter get hot?
Your FM transmitter is overheating and you’re worried about damage or fire hazards. Excessive heat reduces transmitter lifespan and can cause sudden failures during broadcasts. Proper cooling and ventilation keep your transmitter running safely for years.
FM transmitters get hot due to normal power dissipation, poor ventilation, or component failures. Proper cooling requires adequate airflow, clean filters, and temperature monitoring. Most heating is normal but excessive heat indicates problems needing immediate attention.
I’ve serviced hundreds of overheating transmitters over my 15 years in broadcasting. Most heat problems come from blocked ventilation or dust buildup. Understanding normal versus dangerous heating helps you maintain reliable operation and prevent costly failures.
What are common problems with FM transmitters?
Your FM transmitter isn’t working properly and you need to identify the issue quickly. Transmitter problems interrupt broadcasts and frustrate listeners who tune away. Recognizing common issues helps you troubleshoot faster and minimize downtime.
Common FM transmitter problems include overheating, power output drops, frequency drift, audio distortion, and high SWR readings. Most issues stem from component aging, poor connections, or environmental factors that affect performance over time.

The most frequent problems I see involve heat-related failures and connection issues. A customer in Ghana had intermittent power drops that we traced to loose coaxial connectors. The connection heated up during transmission, creating resistance that reduced power output and caused more heating.
Power output problems often indicate aging transistors or power supply issues. Our RS transmitters use high-quality MOSFET transistors rated for continuous operation at full power. These components typically last 5-10 years with proper cooling and maintenance.
Audio quality problems usually come from input processing or modulation circuits. Digital transmitters like our RS-FM1000W eliminate many analog audio issues through DSP processing. The digital approach provides cleaner sound and more stable operation compared to older analog designs.
| Problem Type | Symptoms | Typical Cause |
|---|---|---|
| Overheating | Hot chassis, shutdowns | Poor ventilation |
| Power drops | Reduced coverage | Component aging |
| Audio issues | Distortion, noise | Input problems |
| Frequency drift | Off-channel operation | Crystal aging |
| High SWR | Protection activation | Antenna problems |
| No output | Dead air | Power supply failure |
Environmental factors cause many transmitter problems. Dust, humidity, and temperature extremes stress components and connections. I recommend monthly cleaning and annual professional maintenance to prevent most common failures.
Our transmitters include comprehensive protection systems that prevent damage from most common problems. Over-temperature protection shuts down the transmitter when internal temperature exceeds 60°C. SWR protection reduces power when antenna problems develop. These features prevent minor issues from becoming major failures.
How to strengthen an FM transmitter?
Your FM transmitter signal isn’t strong enough to reach your target coverage area. Weak signals lose listeners to competing stations with better coverage. Strengthening your transmitter system increases audience reach and improves signal quality for existing listeners.
Strengthen FM transmitters by optimizing antenna systems, upgrading power output, improving grounding, and reducing system losses. Professional installation and quality components can double coverage area without changing transmitter power through better efficiency.

The biggest signal improvements come from antenna system optimization rather than just increasing transmitter power. I helped a church station in rural Kenya go from 8-mile coverage to 22-mile coverage by raising their antenna from 30 feet to 100 feet and upgrading to low-loss coaxial cable.
System efficiency determines how much of your transmitter power actually reaches listeners. Poor cables, bad connections, and impedance mismatches waste power as heat instead of useful signal. Quality installation can improve system efficiency from 60% to 95%, effectively doubling your coverage.
Our RS transmitters provide adjustable power output that helps optimize performance for your specific installation. The RS-FM2000W adjusts from 0-2000 watts in precise steps. You can start at lower power for testing and increase gradually to find optimal levels for your coverage goals.
| Improvement Method | Signal Gain | Installation Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Antenna height increase | +6-10 dB | High |
| Low-loss cable upgrade | +2-4 dB | Medium |
| Professional grounding | +1-3 dB | Low |
| Power output increase | Variable | High |
| Antenna gain upgrade | +3-6 dB | Medium |
| System tuning | +1-2 dB | Low |
Ground system quality affects signal strength more than most people realize. Poor grounding creates losses and distorts antenna patterns. A customer in Mexico gained 4 dB signal strength just by installing proper copper ground radials around their antenna base.
Transmitter location matters for signal strength. Higher elevations provide better coverage even with the same antenna height. Moving a transmitter site from a valley to a hilltop can improve coverage by 50-100% without changing equipment. Site surveys help identify optimal locations for maximum coverage.
How to improve FM transmitter quality?
Your FM transmitter audio doesn’t sound as good as commercial radio stations. Poor audio quality makes your station sound unprofessional and amateur. Professional sound quality keeps listeners engaged and builds credibility for your broadcasting operation.
Improve FM transmitter quality through proper audio processing, digital modulation, clean power supplies, and professional installation. Modern DSP transmitters provide broadcast-quality sound that rivals major radio stations at affordable prices.

Audio quality improvements require addressing the complete signal chain from input to antenna. Poor quality at any stage degrades the final output. I’ve seen stations transform their sound quality with simple changes to input levels and processing settings.
Our newer RS transmitters use advanced DSP technology that automatically optimizes audio quality. The digital processing includes pre-emphasis, stereo encoding, and FM modulation all handled in software. This eliminates the noise and distortion common in analog transmitters while providing consistent sound quality.
Power supply quality directly affects audio performance. Clean, stable DC power prevents hum, noise, and modulation artifacts that degrade sound quality. Our transmitters use switched-mode power supplies with excellent regulation and low noise specifications.
| Quality Factor | Improvement Method | Impact Level |
|---|---|---|
| Audio clarity | DSP processing | High |
| Signal stability | Clean power supply | High |
| Frequency accuracy | Crystal oscillator | Medium |
| Stereo separation | Phase alignment | Medium |
| Dynamic range | Compression/limiting | High |
| Background noise | Input filtering | Medium |
Professional installation ensures optimal transmitter performance. Proper grounding, shielding, and cable routing prevent interference and noise pickup. A customer in Tanzania improved their audio quality dramatically just by relocating their transmitter away from computer equipment that was causing RF interference.
Regular maintenance keeps transmitter quality at peak levels. Dust buildup affects cooling and can create arcing that generates noise. Annual cleaning and calibration maintain like-new performance for years. Our 5-year warranty reflects confidence in long-term quality and reliability.
What causes interference with FM transmitters?
Your FM transmitter is causing or receiving interference that disrupts broadcasts. Interference creates poor reception and legal problems with other services. Understanding interference sources helps you operate cleanly and maintain good neighbor relations.
FM transmitter interference comes from harmonics, spurious emissions, intermodulation, and external sources. Proper filtering, shielding, and frequency coordination prevent most interference issues while ensuring regulatory compliance.
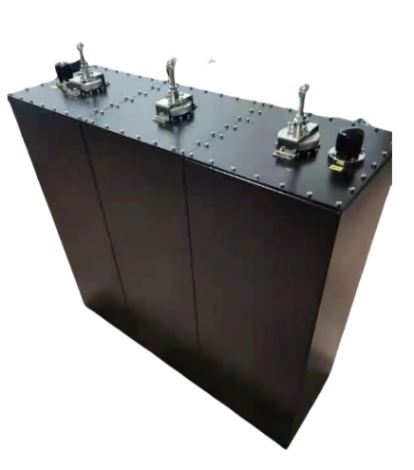

RS-cavity filter
Interference problems fall into two categories: interference you cause to others and interference others cause to you. Both types require different solutions but similar troubleshooting approaches. Proper equipment design and installation prevent most interference issues before they start.
Harmonic interference occurs when your transmitter generates signals at multiples of your operating frequency. A 100 MHz transmitter might interfere with aircraft communications at 200 MHz if harmonic filtering is inadequate. All RS transmitters include built-in harmonic filters that exceed regulatory requirements.
External interference sources include computers, LED lights, switching power supplies, and other electronic devices. These sources generate broadband noise that degrades FM reception. Physical separation and shielding usually solve external interference problems.
| Interference Type | Source | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Harmonics | Transmitter output | Low-pass filtering |
| Spurious signals | Poor design | Quality equipment |
| Intermodulation | Multiple transmitters | Frequency coordination |
| External RFI | Electronic devices | Shielding/separation |
| Adjacent channel | Nearby stations | Proper filtering |
| Overload | Strong signals | Input attenuators |
Proper antenna installation reduces both transmitted and received interference. Vertical separation between transmit and receive antennas prevents desensitization. Horizontal separation reduces coupling between antennas on the same tower.
Our transmitters meet or exceed all international standards for spurious emissions and harmonic suppression. The built-in filtering systems ensure clean operation that won’t interfere with other services. Regular compliance testing verifies continued clean operation over the transmitter’s lifetime.
Conclusion
FM transmitter heating is normal during operation but excessive heat indicates ventilation or component problems. Regular maintenance, proper installation, and quality equipment ensure reliable broadcasting with minimal interference and maximum coverage.



